Gravitational wave recognitions propose combining dark gaps fell into ‘prohibited’ scope of masses.
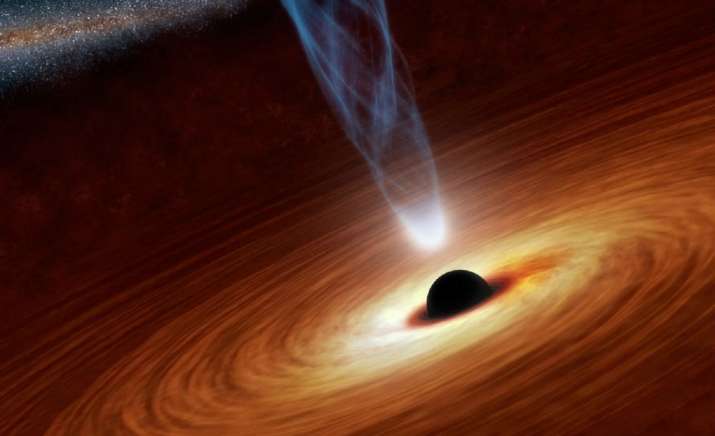
Stargazers have identified the most remarkable, generally far off and most confusing impact of dark holes yet utilizing gravitational waves. Of the two behemoths that melded when the Universe was a large portion of its present age, at any rate one — weighing 85 fold the amount of as the Sun — has a mass that was believed to be too huge to possibly be associated with such an occasion. Furthermore, the merger created a dark gap of almost 150 sun oriented masses, the specialists have assessed, placing it in a range where no dark gaps had ever been definitively observed previously.
“Everything about this discovery is mindboggling,” says Simon Portegies Zwart, a computational astrophysicist at Leiden University in the Netherlands. Specifically, he says, it affirms the presence of ‘middle mass’ dark openings: protests substantially more enormous than a run of the mill star, however not exactly as large as the supermassive dark gaps that possess the focuses of worlds.
Ilya Mandel, a hypothetical astrophysicist at Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, calls the finding “wonderfully unexpected”.
The occasion, portrayed in two papers distributed on 2 September1,2, was recognized on 21 May 2019, by the twin Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Antenna (LIGO) finders in the United States and by the littler Virgo observatory in Italy. It is named GW190521 after its location date.
Forbidden masses
Since 2015, LIGO and Virgo have given new experiences into the universe by detecting gravitational waves. These waves in the texture of room time can uncover occasions, for example, the mergers of dark gaps that would not ordinarily be noticeable with customary telescopes.
From the properties of the gravitational waves, for example, how they change in pitch, astrophysicists can appraise the sizes and different highlights of the articles that delivered them as they were spiraling into one another. This has reformed the investigation of dark openings, giving direct proof to many these articles, running in mass from a couple to around multiple times the mass of the Sun.
These masses are steady with dark gaps that framed in a ‘conventional’ way — when a huge star runs out of fuel to consume and crumples under its own weight. However, the customary hypothesis says that heavenly breakdown ought not deliver dark gaps between around 65 and 120 sun powered masses. That is on the grounds that towards the finish of their lives, stars in a specific scope of sizes become so hot in their focuses they that they begin changing over photons into sets of particles and antiparticles — a marvel called pair unsteadiness. This triggers the touchy combination of oxygen cores, which tears the star separated, totally crumbling it.
In their most recent disclosure, the LIGO and Virgo identifiers detected just the last four waves created by the spiraling dark gaps, with a recurrence that rose from 30 to 80 Hertz inside one-tenth of a second. While moderately littler dark gaps proceed to ‘trill’ up to higher frequencies, extremely huge ones consolidation prior, and scarcely enter the lower end of the recurrence range to which the finders are delicate.
For this situation, the two items were assessed to weigh around 85 and 66 sun based masses. “This is quite neatly in the range one would expect the pair-instability mass gap should be,” says LIGO astrophysicist Christopher Berry of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois.
Selma de Mink, an astrophysicist at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, procrastinates on the cut for pair insecurity even lower, maybe at 45 sun powered masses, which would push the lighter of the two articles solidly into the illegal zone, as well. “For me, both black holes are uncomfortably massive”, she says.
Eccentric dark holes
To clarify their perceptions, the LIGO scientists thought about a scope of potential outcomes, including that the dark openings had been around since the get-go. For quite a long time, specialists have guessed that such ‘primordial’ dark openings could have unexpectedly framed in an expansive scope of sizes soon after the Big Bang.
The fundamental situation the group considered is that the dark gaps got so enormous on the grounds that they were themselves the aftereffect of prior dark opening mergers. Dark gaps coming about because of heavenly breakdown ought to abound inside thick heavenly bunches, and on a fundamental level they could go through rehashed mergers. Be that as it may, even this situation is tricky on the grounds that, following a first merger, the subsequent dark opening ought to commonly get a kick from the gravitational waves and launch itself from the group. Just in uncommon cases would the dark gap remain in a territory where it could go through another merger.
Progressive mergers would be almost certain if the dark gaps occupied the jam-packed focal district of their system, de Mink says, where gravity is sufficiently able to forestall pulling back articles from shooting out.
It isn’t known in which world the merger occurred. Yet, in generally in a similar locale of the sky, a group of specialists recognized a quasar — a very brilliant galactic focus controlled by an excessively huge dark gap — going through a flare around a month after GW1905213. The flare could have been a shockwave in the quasar’s hot gas created by the pulling back dark opening, albeit numerous space experts are wary to acknowledge that the two wonders are connected.
This is the second time this year that the LIGO–Virgo coordinated effort has swam into in a ‘forbidden’ mass range: in June, they depicted a merger including an object of about 2.6 sun based masses — regularly believed too light to ever be a dark gap yet too gigantic to be in any way a neutron star4.

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago