Quantum processing could alter our reality. It promises to be exponentially faster than the zero-or-one binary technology that powers today’s machines, from supercomputers in labs to smartphones in our pockets, for specific and crucial tasks. However, in order to develop quantum computers, a stable network of qubits—also known as quantum bits—is needed to store information, access it, and carry out computations.
However the qubit stages disclosed to date have a typical issue: They will quite often be fragile and powerless against outside unsettling influences. Trouble can be caused by even a stray photon. The final solution to this problem might be to create fault-tolerant qubits that are unaffected by external disturbances.
A significant advancement in this endeavor has been announced by a group led by engineers and scientists from the University of Washington. In a couple of papers distributed June 14 in Nature and June 22 in Science, the specialists report that in tries different things with pieces of semiconductor materials — each main a solitary layer of particles thick — they recognized marks of “fragmentary quantum odd Corridor” (FQAH) states.
The group’s revelations mark a first and promising move toward developing a sort of issue lenient qubit in light of the fact that FQAH states can have anyons — weird “quasiparticles” that have just a small portion of an electron’s charge. Anyons can be used to create qubits that are stable in the face of even the smallest, local disturbances. These qubits are referred to as “topologically protected.”
“This truly lays out another worldview for concentrating on quantum physical science with partial excitations later on,” said Xiaodong Xu, the lead scientist behind these disclosures, who is likewise the Boeing Recognized Teacher of Physical science and a teacher of materials science and designing at the UW.
The exotic fractional quantum Hall state, which is found in two-dimensional systems, is related to FQAH states. Electrical conductivity is restricted to specific fractions of a constant called the conductance quantum in these states. However, fractional quantum Hall systems can’t be used for quantum computing because they need a lot of magnetic fields to stay stable. The team claims that the FQAH state is stable even “at zero magnetic field” and does not have this requirement.
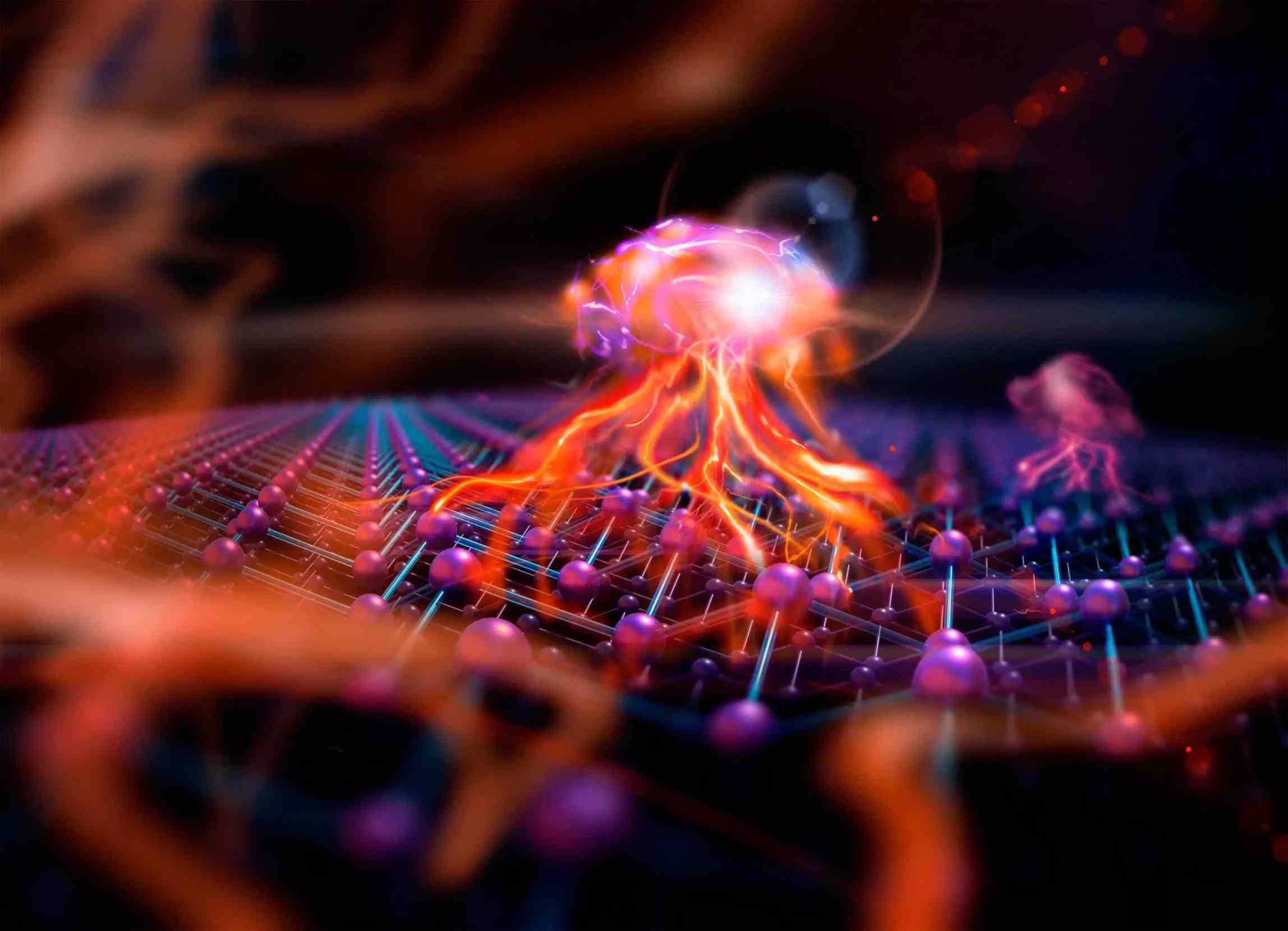
Facilitating such a colorful period of issue expected the specialists to fabricate a counterfeit cross section with outlandish properties. They stacked two molybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2) atomically thin flakes in close proximity to one another at small “twist” angles. A synthetic “honeycomb lattice” for electrons was created by this arrangement.
An intrinsic magnetism was observed in the system when the stacked slices were cooled to a few degrees above absolute zero by the researchers. The natural attraction replaces major areas of strength for the field normally expected for the partial quantum Corridor state. Involving lasers as tests, the specialists recognized marks of the FQAH impact, a significant step in the right direction in opening the force of anyons for quantum registering.
The team, which also includes researchers from Boston College, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the National Institute for Materials Science in Japan, the University of Hong Kong, and the University of Hong Kong, sees their system as a powerful way to learn more about anyons, which are very different from ordinary particles like electrons.
Anyons are quasiparticles — or molecule like “excitations” — that can go about as parts of an electron. In future work with their exploratory framework, the specialists desire to find a considerably more fascinating rendition of this kind of quasiparticle: ” non-Abelian” anyons, which could be utilized as topological qubits. An entangled quantum state can be produced by wrapping the non-Abelian anyons around one another, or “braiding” them. Topological qubits are based on this quantum state, which is a significant improvement over the capabilities of current quantum computers because information is effectively “spread out” throughout the entire system and resistant to local disturbances.
“This sort of topological qubit would be on a very basic level not the same as those that can be made now,” said UW physical science doctoral understudy Eric Anderson, who is lead creator of the Science paper and co-lead creator of the Nature paper. ” Non-Abelian anyons would be much more stable as a platform for quantum computing because of their strange behavior.
FQAH states were able to emerge because the researchers’ experimental setup had three key properties that all existed simultaneously:
Magnetism: However MoTe2 is definitely not an attractive material, when they stacked the framework with positive charges, a “unconstrained twist request” — a type of attraction called ferromagnetism — arose.
Topology: Electrical charges inside their framework have “contorted groups,” like a Möbius strip, which helps make the framework topological.
Interactions: The charges inside their exploratory framework interface emphatically enough to balance out the FQAH state.
The team hopes that this new method will lead to the discovery of non-Abelian anyons.
Jiaqi Cai, co-lead author on the Nature paper and co-author on the Science paper, a doctoral student in physics at the University of Washington, said, “The observed signatures of the fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect are inspiring.” The productive quantum states in the framework can be a research center on-a-chip for finding new material science in two aspects, and furthermore new gadgets for quantum applications.”
“Our work gives obvious proof of the long-looked for FQAH states,” said Xu, who is likewise an individual from the Sub-atomic Designing and Sciences Foundation, the Organization for Nano-Designed Frameworks and the Perfect Energy Establishment, all at UW. ” We are presently chipping away at electrical vehicle estimations, which could give immediate and unambiguous proof of partial excitations at zero attractive field.”
The group trusts that with their methodology, exploring and controlling these strange FQAH states can become ordinary — speeding up the quantum processing venture.


 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Entertainment4 weeks ago
Entertainment4 weeks ago
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago
 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks ago